What is Fiber Channel : Fiber Channel technology has evolved to the point in which Fiber Channel is part of a trend toward convergence between Local Area Network (LAN) and channel technologies. LAN is used to connect computer to computer. While Fiber Channel technology is used to connect computers to high-speed, highly efficient links for them Long term storage devices.
There are different ways to connect a storage system to a server and computer: DAS, SAS, NAS, SAN.
The DAS concept describes the classic solution: The storage is built in the server, it is accessed via the internal bus (e.g. EIDE, S-ATA,SCSI).
The NAS concept separates the storage system (e.g. RAID), the server connects its disks over the existing LAN (e.g. Ethernet).
The SAN concept is the next level, now all storage systems are interconnected together and each server can access each storage system – that´s the "storage area network“. To understand properly, see the image below.
Full name of NAS is Network Attached Storage. In NAS dedicated file server connected to LAN. Use NFS protocol or CIFS. File location is transparent for user.
Separating ownership of a server from its storage, and placing all the storage devices directly on a Fiber Channel network, allows a many-to-many connection from servers to storage and from storage to other storage devices.
This approach grants the benefits of increased scalability, availability, and performance. In addition, backups can be done without affecting the rest of the network since the back-up traffic is done over a separate SAN in a LAN-free backup.
Both options, namely SANs and NAS, have their relative strengths and weaknesses. The primary benefits of SAN include speed and reliability, centralization, and data protection. opposite of this, the main strengths of NAS are interoperability of products from different hardware and operating software vendors, resulting in the overall lower cost of ownership and simplicity.
➤Server/storage independence.
➤Storage device is in a pool of resources accessed by all the servers.
➤Logical distribution of the data within the resources
➤Data service virtualization, sharing, protection and disaster recovery
➤Data transferred through Fiber Channel
➤Protocol and switches (Fabrics).
➤Fiber Channel allow many well-known existing channel and networking protocols to run over the same physical interface and media.
➤High bandwidth (100 Mbps and beyond).
➤Flexible topology.
➤Connectivity over several kilo-meters.
➤Support for multiple data rates, media types, and connectors.
➤ Standard for serial transmission of data
• ANSI working group X3T11, X3T9.3 und X.3230
• FCIA Fiber Channel Industry Association
➤ Belongs to categories of SCSI, ATA, S-ATA, iSCSI, (Ethernet), (ATM),
➤ It´s not only
• a line connection using fibers
• a networking technology (only to transmit data from A to B)
• a storage solution
• a future topic, but a well known standard (ANSI since 1994, products since 1992)
• similar to ESCON and FICON.
Fiber channel knows different ways of connection services:
FC-Class 1: Dedicated Circuit
Means circuit switched connection, used for traditional services like voice (ISDN, POTS). A complete channel is switched from source to destination and fixed for a specific period of time.
FC-Class 2: packet based, switched transfer with Control
Means packet based transfer with connection control by the user. Each user knows „packet-request“ and „packet-acknowledgement“. , each packet is switched from source to destination. The channel is available for multiple users: Multiplexing.
FC-Class 3: Data-gram / packet based, switched transfer without Control
Means packet based transfer, each packet is switched from source to destination. The channel is available for multiple users: Multiplexing.
Fiber Channel allows an intermix of circuit and packet switching.In fiber channel high transmission speed of circuits combined with flexibility of networks.
Striping: In stripping it is to multiply bandwidth using multiple N ports in parallel to transmit a single information unit across multiple links.
Hunt groups: In hunt group this is the ability for more than one port to respond to the same alias address. This improves efficiency by reducing the chance of reaching a busy N port.
Multicast: Multicast delivers a single transmission to multiple destinations ports. This includes sending to all N ports on a Fabric (broadcast) or to only a subset of N ports on a Fabric.
FC-4 (Application)
➤In the FC structure the highest level , defines the application interfaces that can execute over Fiber Channel.
➤Specified the mapping rules of upper layer protocols using the Fiber Channel levels below
➤Allows to adapt both - Networks ( 802.2, IP, ATM)- Channels ( IPI, SCSI, HIPPI, SBCCS).
FC-4 (Application)
➤Fibre Connection announcement on IBM S/390 servers in 1998.
➤Improvement of ESCON.
➤Bridge mode to map ESCON.
➤Native mode FICON channel on server & FICON interface adapter on Control Unit.
➤FICON is a Data transmission protocol based on ANSI Fiber Channel System FC-SB-2 based on SBCCS protocol.
➤Used by open systems server and storage vendors.
➤Supported on IBM S/390 , Z Architecture systemes ,& Wintel, Linux, UNIX.
Transponder is changing only the wavelength, no switch (layer 2) functionality. At the far end the signal can be looped by cable (“hard loop”, “physical loop”)
2802 test set-up:
Depending on the distance to brigde
> till 10km (without credit buffers) select Layer 1
> above 10km (with credit buffers) select Layer 2 because of login process
The classical networking technologies like Ethernet did n'´t fit the special needs of storage system. So a specialized technology was developed to interconnect storage systems (disks and tapes) with computers: Fiber Channel. The introduction and popularity of the term storage area network (SAN), a network highly adapted for transferring data between computers and storage devices, has contributed to the success of Fiber Channel Technology.
Introduction of Fiber Channel
Modern information systems require high capacity storage which has to fit a lot of special needs: Storage access has to be fast and reliable. Security considerations drive to locate the storage systems in computer centers and to double them. For disaster recovery reasons the online and backup storage systems are split to different locations. And much more.There are different ways to connect a storage system to a server and computer: DAS, SAS, NAS, SAN.
The DAS concept describes the classic solution: The storage is built in the server, it is accessed via the internal bus (e.g. EIDE, S-ATA,SCSI).
The NAS concept separates the storage system (e.g. RAID), the server connects its disks over the existing LAN (e.g. Ethernet).
The SAN concept is the next level, now all storage systems are interconnected together and each server can access each storage system – that´s the "storage area network“. To understand properly, see the image below.
 |
| DAS,SAN and NAS |
Now I am trying to explain in detail about DAS, SAS, NAS, SAN so that you all get complete information. While writing the article, I try my best not to put such things in front of you which is different from the topic.
Storage DAS & SAS
DAS as you can understand, which full name is, Direct Attached Storage or SAS server attached storage. In the DAS or SAS storage one storage device directly attached to server bus via adapter. SAS or DAS perform simple I/O operation, caching, or dual copy of data. It is not better to write a long theory about it, to understand it better, see the image below. |
| DAS and SAS storage |
Storage NAS
Several 100 user could work per NAS . Manage I/O request , queuing and security.
In NAS storage grew out of the concept of file servers managing the files for clients on the network. This approach achieved tremendous success through products such as Net-Ware and Microsoft Windows NT Server. With file servers, large amounts of storage could be connected from the server and served to users on a file-by-file basis, while management and backup of that data could be centralized off the server.
Over time as technology developed it became clear that a full network operating system was not necessary for file services.. As a result of this, vendors designed a specialized server and operating system, called a storage device, that could be placed on the network to provide a storage function. For full understanding, see the image below.
 |
| Fiber Channel Storage NAS |
SAN Storage Area Network
Storage area networks emerged from the concept of taking storage devices and storing heavy traffic and creating a separate back end network designed specifically for that kind of traffic.Separating ownership of a server from its storage, and placing all the storage devices directly on a Fiber Channel network, allows a many-to-many connection from servers to storage and from storage to other storage devices.
This approach grants the benefits of increased scalability, availability, and performance. In addition, backups can be done without affecting the rest of the network since the back-up traffic is done over a separate SAN in a LAN-free backup.
Both options, namely SANs and NAS, have their relative strengths and weaknesses. The primary benefits of SAN include speed and reliability, centralization, and data protection. opposite of this, the main strengths of NAS are interoperability of products from different hardware and operating software vendors, resulting in the overall lower cost of ownership and simplicity.
➤Server/storage independence.
➤Storage device is in a pool of resources accessed by all the servers.
➤Logical distribution of the data within the resources
➤Data service virtualization, sharing, protection and disaster recovery
➤Data transferred through Fiber Channel
➤Protocol and switches (Fabrics).
SAN versus NAS
Many IT organizations are contemplating network implementations that revolve around storage networks. Two popular terms in the market are SAN (storage area network) and NAS (network-attached storage).
The two concepts are different in their network implementations and advantages and disadvantages exist for both approaches. The debate is still on as to which implementation will prevail.
Fiber Channel Topology
In Fiber Channel technology there are three type of topology- (a) Point to Point Topology (b) Fabric Topology (c) Loop Topology. FC-0 layer describes the link between two ports. It is important to mention one thing here the link consists of a pair of optical fibers or electrical cables.
Given that the FC-0 layer is designed for maximum flexibility, it allows the use of a wide variety of technologies to meet a range of system requirements. Switches connecting devices are called fabric. The link between the two devices consists of two unidirectional fibers that transmit in opposite directions. Each fiber is connected to the transmitter of a node port (N_Port) at one end and the receiver of the other N_Port at the other end.
When the fabric is present in the configuration, many ports are connected. The fiber may be connected to a port of N_Port and fabric (F_Port).
In addition, the loop topology allows multiple ports to be joined together without a routing switch. The topology can be chosen based on system performance requirements. To understand properly, see the image below.
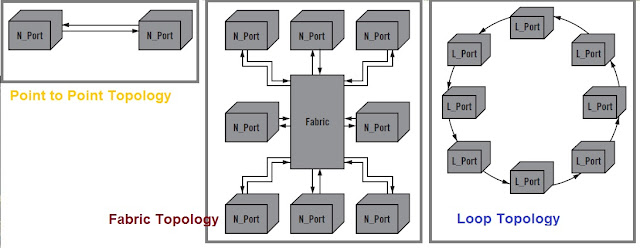 |
| P2P,Fabric and Loop Topology |
The Goals of Fiber Channel
By now we know that fiber channel is a protocol designed to full-fill many requirements related to the increasing demand for high performance information transfer. Fiber Channel goals include-➤Fiber Channel allow many well-known existing channel and networking protocols to run over the same physical interface and media.
➤High bandwidth (100 Mbps and beyond).
➤Flexible topology.
➤Connectivity over several kilo-meters.
➤Support for multiple data rates, media types, and connectors.
In general, Fiber Channel attempts to combine the benefits of both channel and network technologies. There are two basic types of data communication between processors and peripherals and between channels: channels and networks.
A channel is a closed, direct, structured and predictive mechanism for transmitting data between relatively few entities. Typically, very few decisions need to be made after a channel is established, thus allowing for a high-speed, hardware intensive environment. Channels are commonly used to connect peripheral devices such as disk drives, printers, tape drives etc.
Now we will try to understand fiber channel and network in some other way also. I think in this way you will be very easy to understand.
As mentioned above the idea behind Fiber Channel was to combine the advantages of existing networking technologies with the advantages of Computer bus systems. The result is a high performance solution with capabilities for real-time applications, long distance transfer without buffer mechanisms. The concept is block oriented transfer. So Fiber Channel can transport SCSI, HIPPI, IPI, IEEE 802.2, IP and ATM.Fiber Channel: Channel + Network
 |
| Fiber channel-Channel-Network |
What is Fiber Channel
Transports data of mass storage systems & protocols.➤ Standard for serial transmission of data
• ANSI working group X3T11, X3T9.3 und X.3230
• FCIA Fiber Channel Industry Association
➤ Belongs to categories of SCSI, ATA, S-ATA, iSCSI, (Ethernet), (ATM),
➤ It´s not only
• a line connection using fibers
• a networking technology (only to transmit data from A to B)
• a storage solution
• a future topic, but a well known standard (ANSI since 1994, products since 1992)
• similar to ESCON and FICON.
FC-Class 1: Dedicated Circuit
Means circuit switched connection, used for traditional services like voice (ISDN, POTS). A complete channel is switched from source to destination and fixed for a specific period of time.
FC-Class 2: packet based, switched transfer with Control
Means packet based transfer with connection control by the user. Each user knows „packet-request“ and „packet-acknowledgement“. , each packet is switched from source to destination. The channel is available for multiple users: Multiplexing.
FC-Class 3: Data-gram / packet based, switched transfer without Control
Means packet based transfer, each packet is switched from source to destination. The channel is available for multiple users: Multiplexing.
Fiber Channel allows an intermix of circuit and packet switching.In fiber channel high transmission speed of circuits combined with flexibility of networks.
 |
| Fiber channel knows different ways of connection services |
I have adopted very easy methods to understand fiber channel topology. I hope you all have no problem in understanding-
 |
| Fiber channel topology port details |
Fiber Channel Rates
It is not better to write a long theory about fiber channel rate. Only you have to look at the given image carefully, everything will make sense-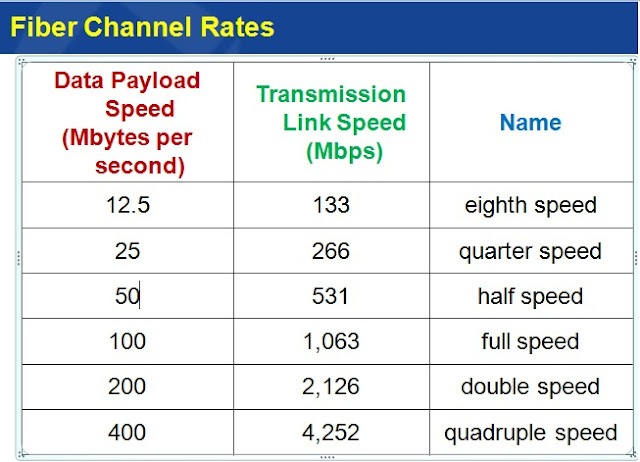 |
| Fiber Channel Rates and Name details |
FC Architecture: Protocol Layers
I do not want to make the article too long, so I try to keep moving forward by telling the whole thing in a very easy way.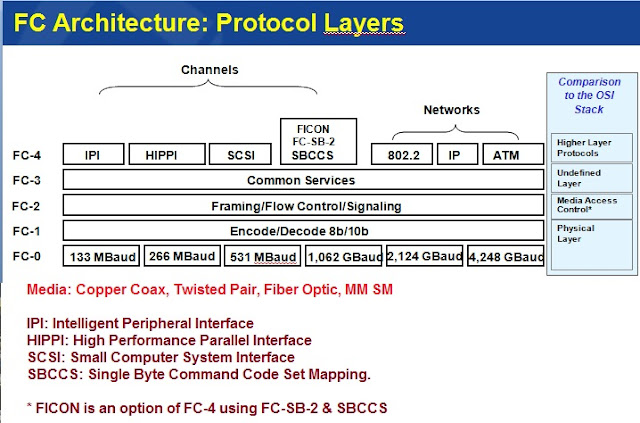 |
| Protocol Layers |
FC-0 (Physical) : FC-0 defines the physical link of the system, including media specifications (fiber, connector), as well as optical and electrical receiver and transmitter parameters for a variety of data rates.
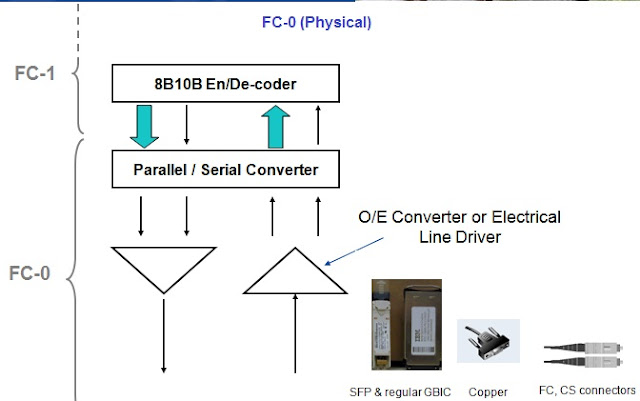 |
| FC-0 |
FC-1 (8B/10B coding) : FC-1 defines the transmission protocol including 8B/10B character encoding and decoding rules, special characters and error control.
FC-1 encodes 8bit information into 10bit transmission character. DC balance and enough transition for clock recovery.
 |
| FC-1 |
FC-2 (Framing & Signaling) : FC-2 serves as the transport mechanism of the Fiber Channel protocol.This layer defines the framing rules, sequence and exchange management,management of services classes, flow control and login.
Variable frame length from 36 to 2148 Bytes. Even multiple of 4 Bytes.
All FC devices have its own unique WWN address (World Wide Name)
Minimum Frame Size (no payload) = 28 bytes (Frame Header + CRC Error Check ) + 8 bytes of Start and End of Frame delimiters.
Maximum Frame Size = 2140 bytes (if optional headers are supported), or 2076 bytes (without optional headers) + 8 bytes of Start and End of Frame delimiters.
FC-2 (Classes of Services):
Class 1: Dedicated connections. Guaranteed bandwidth.Frames delivered in order
Class 2: Frame-switched, connection-less service. Bandwidth shared by frame multiplexing. Frames may be delivered out of order. Guaranteed delivery (Acks and re-transmissions).
Class 3: Datagram service. Send and Pray. Neither order nor delivery is guaranteed.
Intermix = Class 1 and 2
Class 4: Partial bandwidth connection oriented service A connection-oriented class of communication service in which a portion of the link's bandwidth between two ports is dedicated to communication between ports.
Class 5: Not defined
Class 6: Simplex Connection Service
A connection-oriented class of communication service between two Fiber Channel ports that provides dedicated unidirectional connections for reliable multicast. Also known as uni-directional dedicated connection service.
FC-3 (Common Services)
For advanced feature-set like:
Hunt groups: In hunt group this is the ability for more than one port to respond to the same alias address. This improves efficiency by reducing the chance of reaching a busy N port.
Multicast: Multicast delivers a single transmission to multiple destinations ports. This includes sending to all N ports on a Fabric (broadcast) or to only a subset of N ports on a Fabric.
➤In the FC structure the highest level , defines the application interfaces that can execute over Fiber Channel.
➤Specified the mapping rules of upper layer protocols using the Fiber Channel levels below
➤Allows to adapt both - Networks ( 802.2, IP, ATM)- Channels ( IPI, SCSI, HIPPI, SBCCS).
➤Fibre Connection announcement on IBM S/390 servers in 1998.
➤Improvement of ESCON.
➤Bridge mode to map ESCON.
➤Native mode FICON channel on server & FICON interface adapter on Control Unit.
➤FICON is a Data transmission protocol based on ANSI Fiber Channel System FC-SB-2 based on SBCCS protocol.
➤Used by open systems server and storage vendors.
➤Supported on IBM S/390 , Z Architecture systemes ,& Wintel, Linux, UNIX.
Fiber Channel Testing
 |
| Fiber Channel Testing details |
2802 test set-up:
Depending on the distance to brigde
> till 10km (without credit buffers) select Layer 1
> above 10km (with credit buffers) select Layer 2 because of login process





4 Comments
Nice post, getting FULL Information at one place its really good,, !!! Planet most love music app mp3 juice get here thanks ....
ReplyDeleteNice post, getting FULL Information at one place its really good,, !!! World most Famous app to make life easier without any problems thanks ....
2691CC84CC
ReplyDeletekiralık hacker
hacker arıyorum
belek
kadriye
serik
3E21EE1E19
ReplyDeleteinstagram takipçi
black swivel accent chair
C5E9544C2F
ReplyDeleteBeğeni Satın Al
Ucuz Takipçi
Instagram Takipçi Kasma