What are the main parts of NSS : Some telecom friends have expressed their wish to provide some information about the NSS. So this is a small attempt from me to gather some information about the NSS. Network switching subsystem is a very big topic in itself but let's talk specifically about the main parts of the NSS.
Mainly GSM Network Architecture divided into three parts- 1. BSS (Base Station Subsystem), 2. NMS (Network Management Subsystem) and 3. NSS ( Network Switching Subsystem ). In this article, the main parts of NSS will be explained.
Authentication Center (AC) and Equipment Identity Register (EIR) are also the part of NSS (Network Switching Subsystem). Security in the GSM network are provided by the use of the Authentication Centre (AC) and Equipment Identity Register (EIR).In the GSM network architecture, what is the role of NSS, an attempt has been made by the following picture.
We have all been well aware that GSM network is divided into three subsystems: Network Switching Subsystem (NSS), Base Station Subsystem (BSS), and Network Management Subsystem (NMS). But right now we're talking only about the main part of the NSS.
NSS which is an important part of GSM architecture has its following parts-
1. MSC (Mobile Services Switching Center)
2. VLR (Visitor Location Register)
3. HLR (Home Location Register)
1. MSC (Mobile Services Switching Center) : It controls many BSCs. The MSC is similar to the heart of GSM architecture. Because it is the most important part of GSM architecture. It manages communication between GSM and other networks.
1. Call Control : The function of NSS is call control, other functions also come under call control such as identifies the subscriber, establishes a call and clears the connection after the conversation is over.
2. Charging : The second main function of NSS is charging. Actually charging is a process and through this process collects the charging information about a call such as the numbers of the caller and the called subscriber, the time and type of the transaction, etc., and transfers it to the Billing Center.
3. Mobility management : By Mobility Management process maintains information about the location of the subscriber.
4. Communication with other networks and the BSS : Through this applies to interfaces with the BSS and PSTN.
5. Subscriber data handling : In Subscriber data handling is the permanent data storage in the HLR and temporary storage of relevant data in the VLR. which already described above.
6. Locating the subscriber : With the help of this process locates a subscriber before establishing a call.
My dear telecom friends, how have you got the information given in the article " main parts of NSS " I have not made this subject very big, according to this subject, only the necessary things have been written. Friends who needs more information about NSS will tell me by commenting.
Mainly GSM Network Architecture divided into three parts- 1. BSS (Base Station Subsystem), 2. NMS (Network Management Subsystem) and 3. NSS ( Network Switching Subsystem ). In this article, the main parts of NSS will be explained.
About NSS ( Network Switching Subsystem ) ?
As mentioned above, the NSS is a part of the GSM network architecture. It contains the elements Mobile Services Switching Center (MSC), Home Location Register (HLR), Visitor Location Register (VLR), Authentication Center (AC), Equipment Identity Register (EIR).Authentication Center (AC) and Equipment Identity Register (EIR) are also the part of NSS (Network Switching Subsystem). Security in the GSM network are provided by the use of the Authentication Centre (AC) and Equipment Identity Register (EIR).In the GSM network architecture, what is the role of NSS, an attempt has been made by the following picture.
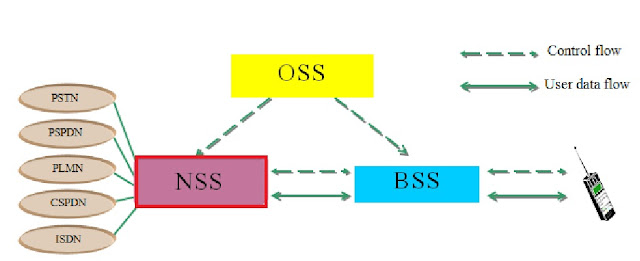 |
| NSS in GSM network architecture |
Main Parts of NSS ( Network Switching Subsystem )
We have all been well aware that GSM network is divided into three subsystems: Network Switching Subsystem (NSS), Base Station Subsystem (BSS), and Network Management Subsystem (NMS). But right now we're talking only about the main part of the NSS.
Below are the main elements of NSS which we will discuss-
➤MSC (Mobile Services Switching Center)
➤VLR (Visitor Location Register)
➤HLR (Home Location Register)
Perhaps the term MSC is not new to all of you, we all know that MSC is responsible for controlling calls in mobile networks, this identifies the origin and destination of the call as well as the type of call.
In GSM network MSC act like as a bridge between a mobile network and a fixed network so it is called a Gateway MSC. MSC is typically integrated with a VLR, which holds information related to customers who are currently in the service area of the MSC. VLR also carries out the location registrations and updates.
MSC begins its paging process with the help of VLR. A VLR database is always temporary, While HLR maintains a permanent register of customers. In addition to fixed data, HLR also maintains a temporary database including the current location of it customers. This data is required for routing calls.
It's better to remind you all here that Authentication Center (AC) and the Equipment Identity Register (EIR) are two more elements in the NSS. Both usually implemented as part of HLR and they deal with the security functions. Now, one by one I will briefly write about the main part of NSS.
NSS which is an important part of GSM architecture has its following parts-1. MSC (Mobile Services Switching Center)
2. VLR (Visitor Location Register)
3. HLR (Home Location Register)
1. MSC (Mobile Services Switching Center) : It controls many BSCs. The MSC is similar to the heart of GSM architecture. Because it is the most important part of GSM architecture. It manages communication between GSM and other networks.
The main tasks taken by MSC in GSM network are call setup, basic switching and call routing etc. And it also performs the function of user registration and authentication.
2. VLR ( Visitor Location Register ) : The VLR is the temporary information about the subscriber and this information is used by the MSC. When a subscriber moves from one location to another, its information is updated in the VLR.
VLR also handles roaming operations, if the customer goes out of his HLR area, then roaming is done by him. The VLR is the same information as the HLR, but its information is temporary while the HLR is permanent.
3. HLR (home location registers) : The HLR keeps the information of all the registered subscribers such as: - Customer id, customer number, billing information, and the information of final recharge etc. And along with that, it also keeps the location information of the subscriber.
EIR (equipment identity register) : The EIR decides whether a mobile will access a network or not. Every mobile has a unique number which we call international mobile equipment identity (IMEI). When the mobile registers in a network, the network checks this number. If the IMEI number is correct, then it will be able to access the mobile network or it will not be able to.
AUC (authentication center) : In other words we can say that AUC is a database of NSS that stores a secret key in each subscriber's SIM card which is used for authentication and encryption. AUC protects subscribers from fraud, fake calls, etc.
Main functions of NSS
Below mentioned are the main function of NSS-1. Call Control : The function of NSS is call control, other functions also come under call control such as identifies the subscriber, establishes a call and clears the connection after the conversation is over.
2. Charging : The second main function of NSS is charging. Actually charging is a process and through this process collects the charging information about a call such as the numbers of the caller and the called subscriber, the time and type of the transaction, etc., and transfers it to the Billing Center.
3. Mobility management : By Mobility Management process maintains information about the location of the subscriber.
4. Communication with other networks and the BSS : Through this applies to interfaces with the BSS and PSTN.
5. Subscriber data handling : In Subscriber data handling is the permanent data storage in the HLR and temporary storage of relevant data in the VLR. which already described above.
6. Locating the subscriber : With the help of this process locates a subscriber before establishing a call.





8 Comments
I need this in more detail
ReplyDeleteThanks for sharing the post.. parents are worlds best person in each lives of individual..they need or must succeed to sustain needs of the family. Lawn Mower Blades
ReplyDeleteReally a great addition. I have read this marvelous post. Thanks for sharing information about it. I really like that. Thanks so lot for your convene. ទិដ្ឋាការអាមេរិកតាមអ៊ីនធឺណិត
ReplyDeletethnks
ReplyDeleteIntegration of device and sensor data with big data, analytics, and other enterprise applications is a core concept behind the emerging IoT. This integration is key to achieving numerous benefits throughout the manufacturing enterprise and, ultimately, growth in the marketplace.
ReplyDeleteESIM cards are embedded in your device, and because they're software-based, they can be easily swapped between different devices. You can also store multiple eSIM profiles on a single device, which is perfect if you have multiple phone numbers or want to use a local SIM card when you're traveling overseas. Mobile SIM card
ReplyDeleteI believe one of your commercials caused my internet browser to resize, you may well want to put that on your blacklist. android 21 lab coat
ReplyDeleteWear Luxerious Style Outfit of Taylor Swift Red Coat Look more beautiful
ReplyDelete