Future development in PON technologies: First of all, we try to know about PON technology. We can say about the PON (Passive Optical Network) in simple words that "Using an optical transmission system, an architecture has been used from the central office to carry signals directly to users and businesses such as multi-dwelling units through fiber optic cable.Passive means that there is no active or operated element between the exchange and the location of the customer".
➤GPON supports several advanced services for revenue growth.
➤It has less plant maintenance and operating costs
➤GPON has cost parity with low bandwidth copper-based network.
➤Through GPON technology provided long reach without amplification.
➤In GPON technology there are no active electronics components in OSP equipment.
➤GPON technology has long physical and economic lifetime.
➤This technology can be fast & quick deployment.
➤GPON technology has easy installation & upgrade.
➤GPON technology permit small diameter & light weight cables thus small space occupancy.
➤GPON technology secure & immune to electromagnetic interference.
Till recently, through the various steps like APON / BPON of development, when the technique reached to the standardizing the last technical name as GPON, so that the needs of bandwidth can be met for business communities as well as for the public.This all developments are the part of future development of PON technology which is now gradually being completed.
 |
| Residential bandwidth trends |
Development of GPON technologies
Gigabit Passive Optical Network - GPON : GPON is a type of Common and Access Networks, for all types of networks, today and future technology. GPON emerges via various PON technologies such as APON, BPON, EPON, and finally standardized by IEEE and ITU. The approach of PON (Passive Optical Network Technology) is different from most of the existing network, which is by the name "Passive" in operation. Active networks such as DSL, ADSL and VDSL have active components in access network infrastructure and in customer base equipment.
GPON has only passive light transmission components in the access network with only the active compenent in the central office and in the customer base equipment. The endpoint in the central office is in the optical line terminal (OLT) equipment. Customer is on optical network terminals or the ONT endpoint. There is a passive optical network between the OLT and ONT, which includes fiber links and passive splitter.
The optical budget of 28dB with GPON technology using class B+ optics enables a reach of 30km when the splitting factor is limited to 1:16. The new class C+ optics add a further 4dB of link budget providing the option of additional distribution splitting capabilities or more reach. GPON technology has capabilities to increase further to 60km reach or 128 end-users.
Although GPON is perceived to possess sufficient bandwidth for the coming years, XG-PON is already standardized. With the result that the limit has not yet been reached and PON parameters will be pushed to higher values.
XG-PON is a natural continuation in the evolution of PON technologies, increasing bandwidth four-fold to 10Gbps, with a reach extending from 20 to 60 km and split from 64 to 128. It should be noted that the split and reach maxima are not obtainable simultaneously. Most importantly, these evolutionary technologies will avoid the need for significant upgrades to the existing outside plant.
The 10G-EPON (10-Gigabit Ethernet PON) standard was ratified in September 2009 under the title of 802.3av. This latest standard offers a symmetric 10Gbps, and is backward compatible with 802.3ah EPON. 10G-EPON uses different wavelengths for 10Gbps and 1Gbps downstream, and will continue to use single wavelengths for both 10Gbps and 1Gbps upstream with TDMA separation of customer data.The 802.3av Task Force has concluded its work, with the 802.3av and will be included in the IEEE 802.3 set of standards.
Next‐generation PON technologies
The next step after XG-PON could involve increasing the line speed of the fibre to 40 or even 100Gbps. Already an alternative to initial deployment is the use of wavelength-division multiplexing (WDM) techniques to send several wavelengths on the same fiber. WDM-PONs promises to combine the best of both worlds – a physical PON network (sharing feeder fibres) with logical point-to-point connectivity (one wavelength per user).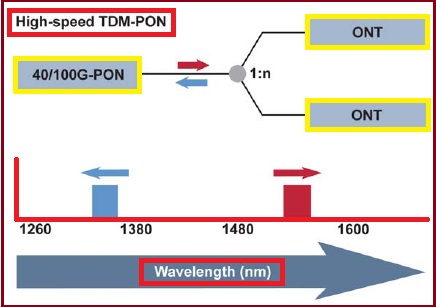 |
| NG-PON technology |
This architecture provides transparent connectivity, devoted to a wavelength on a per customer basis. The result is the provision of very-high, uncontended bit rates for each connected subscriber offering the same inherent security as dedicated fiber. These architectures use wavelength filters instead of splitters in the field to map each wavelength from the feeder fiber onto a dedicated drop fiber. In last, it is a logical upgrade path from current TDM-PON deployments to WDM-PON at the level of physical infrastructure.
The important challenge for WDM-PON is to provide various upstream wavelengths while being a single ONU type. Communications providers consider it unmanageable to have a different ONU per wavelength, and tuneable lasers are so far not affordable. The technologies required for WDM-PON are available today, but reduction in costs is necessary if they are to be considered suitable for mass deployment.
 |
| Next Generation PON technology |
A third possibility is stacking several TDM-PON signals on one fibre, typically a combination of four XG-PON systems running at 10Gbps each. This is called hybrid TDM-WDM-PON.
 |
| Development of PON technology |
Benefits of Gigabit Passive Optical Networks (GPON)
➤More bandwidth capacity provided for the subscriber.➤GPON supports several advanced services for revenue growth.
➤It has less plant maintenance and operating costs
➤GPON has cost parity with low bandwidth copper-based network.
➤Through GPON technology provided long reach without amplification.
➤In GPON technology there are no active electronics components in OSP equipment.
➤GPON technology has long physical and economic lifetime.
➤This technology can be fast & quick deployment.
➤GPON technology has easy installation & upgrade.
➤GPON technology permit small diameter & light weight cables thus small space occupancy.
➤GPON technology secure & immune to electromagnetic interference.




0 Comments