Why should Optical network called Agile Optical Network (AON): An agile optical network (AON) is a dynamically reconfigurable DWDM network that is designed to accelerate triple-play service deployment, simplify network management, and enable advanced wavelength applications at significantly reduced costs..The key element of the AON is dynamic reconfigurable, or the ability for service providers to optimize network activity via optical equipment within the network that can be monitored and adjusted remotely.
The challenges such services present call for optical communication innovation that replaces slow, manual operational processes with simplified, dynamic network configuration and automated service provisioning. Telecom companies are upgrading their architectures to support voice, video, and data within a single network. Telecom companies and cable operators are also converging into a single market, competing to offer voice, video, and data services to consumers on a single bill. It gives you agile and modern optical networking that supports all your airport-related communications. Below image shows the topology of a typical AON.
Key benefits of the Agile Optical Network AON
Challenges of Agile Optical Network (AON)
Each component of the AON will evolve through technology breakthroughs and continue to provide the flexibility networks require. As more flexibility is built in, service providers can consider their “fear of the next YouTube” a thing of the past. We can say that Agile Optical Network (AON) grow the broadband users.
➠Broadband users grow from 32 million lines in 2004 to nearly 57 million lines in 2008.
➠VoIP lines in the United States grow from 6.5 million in 2004 to 26 million in 2008.
➠VoD streams worldwide will explode from 1.67 million in 2005 to 163 million in 2011.
➠About 66% of online consumers in the United States log on daily, and an additional 16% log on several times a week for entertainment. Still grow day by day.
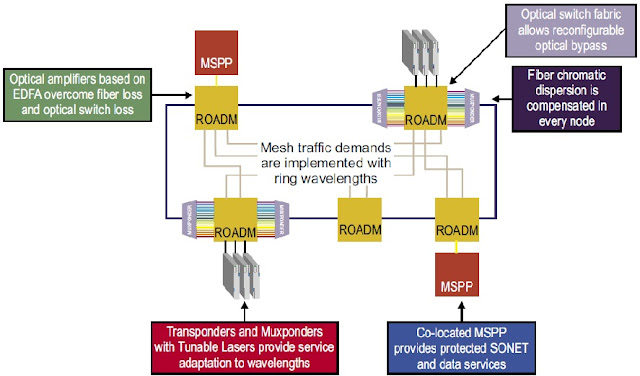 |
| AON Network |
Why should Optical network called Agile Optical Network (AON)
New uses for the Internet are creating a disruptive and unpredictable environment for networks. The popularity of video-on-demand (VoD), voice over IP (VoIP), IPTV, and other emerging applications is driving an ever-increasing need for flexible, fast, and high-quality network services.
Increased service velocity via a dynamically reconfigurable topology
➽Provision new services
➽Reconfigure the topology using a “point-and-click” remote network management system (NMS)
Advanced wavelength services
➽Provision new services
➽Reconfigure the topology using a “point-and-click” remote network management system (NMS)
➽Private line services at dedicated bandwidths and wavelengths
➽Bandwidth on demand
➽Wavelength on demand
➽Bandwidth on demand
➽Wavelength on demand
Accelerated triple-play services
➽Flexible
➽Scalable
➽Simplified management
➽Flexible
➽Scalable
➽Simplified management
Reduced operating and capital expenses
➽Reduction of expensive O-E-O
➽Optimized capacity
➽Fewer truck rolls
➽Reduction of sparing/inventory
➽Increased the supply chain velocity and simplicity
➽Increased quality of service through performance monitoring, fault detection, and automatic healing
We can say that benefits of the Agile Optical Network (AON) is Wavelengths can be remotely configured dynamically in reconfigurable optical add/drop multiplexer (ROADM) nodes.Time for wavelength provisioning is reduced, typically from weeks or months to a few hours or days.Efficiencies required for triple play, especially IPTV services, are enabled. Capabilities required for dynamic wavelength services are provided. Time-to-service revenue decreases. Automation and/or automatic functions are provided through “points of agility.”Resilience to respond to spontaneous bandwidth demands is provided; errors in the planning process are compensated.
➽Reduction of expensive O-E-O
➽Optimized capacity
➽Fewer truck rolls
➽Reduction of sparing/inventory
➽Increased the supply chain velocity and simplicity
➽Increased quality of service through performance monitoring, fault detection, and automatic healing
The migration from fixed point-to-point networks toward dynamic wavelength switching meshed networks has created a number of challenges.
Wavelength management
➠Wavelength ID (pilot tones)
➠Wavelength route loss and continuity
Wavelength management
➠Wavelength ID (pilot tones)
➠Wavelength route loss and continuity
Intensity management
➠Transient, dynamic wavelength switching testing (OAM transient response)
➠Power levels and gain equalization testing
Performance management
➠OSNR testing (in-band OSNR)
➠Dispersion testing (in-service, in channel CD and PMD)
➠Electrical and optical amplification sampling (Q-factor)
➠Transient, dynamic wavelength switching testing (OAM transient response)
➠Power levels and gain equalization testing
Performance management
➠OSNR testing (in-band OSNR)
➠Dispersion testing (in-service, in channel CD and PMD)
➠Electrical and optical amplification sampling (Q-factor)
Fiber characterization
➠Continuity and loss testing (tunable OTDR)
➠CD and PMD testing (through ROADMs, for example).
➠Continuity and loss testing (tunable OTDR)
➠CD and PMD testing (through ROADMs, for example).
In the Agile Optical Network AON, each channel may traverse through different routes, optical amplifiers, and add-drop filters. Even adjacent channels may have a different noise level. Therefore, the measurement of the OSNR in these networks is not possible using the conventional linear interpolation technique.
➠Broadband users grow from 32 million lines in 2004 to nearly 57 million lines in 2008.
➠VoIP lines in the United States grow from 6.5 million in 2004 to 26 million in 2008.
➠VoD streams worldwide will explode from 1.67 million in 2005 to 163 million in 2011.
➠About 66% of online consumers in the United States log on daily, and an additional 16% log on several times a week for entertainment. Still grow day by day.




0 Comments