 |
| BSC |
Transmission Methods Between BSC and BTS: Today I would like to share the details about how BSC communicate to a BTS? Means Transmission between BSC and BTS in GSM network. Always I try to provide the basic knowledge of telecommunication. If you feel that I have provided some knowledge to you, then share it with your friends/groups and subscribe to www.technopediase.com. Also comment about the post,I will feel better with your feedback.
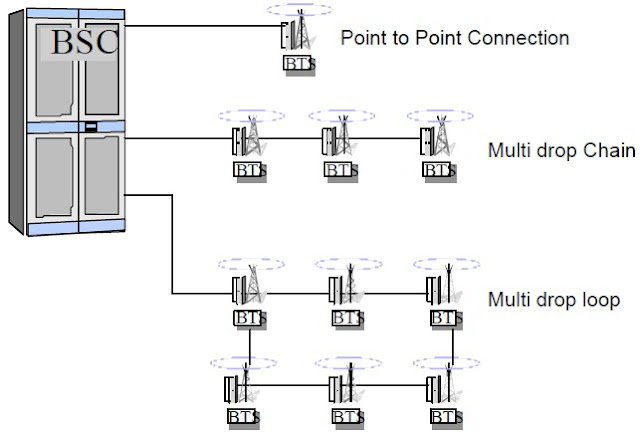
Now I am coming to the topic " Transmission Methods Between BSC and BTS" There are three alternative methods to provide the connections between a BSC and several BTSs. The method used will depend on a number of factors such as the distance between the Base Station Controller (BSC) and Base Transceiver Station (BTS), the number of TRXs used at a particular BTS site, the signalling channel rate between Base Station Controller (BSC) and Base Transceiver Station (BTS). There are three options available: point-to-point connection, multidrop chain and multidrop loop.
 |
| Connection method between BSC and BTS |
Transmission Methods Between BSC and BTS
One by one I will discuss about the Transmission Methods Between BSC and BTS: point-to-point connection, multidrop chain and multidrop loop.
Point-to-point connection
Point-to-point connection indicates that the Base Station Controller (BSC) is connected directly to every BTS with a 2Mbit/s PCM line. This is a simple and effective method particularly in cases when the distance between BSC and BTS is short. However, if the BSC -BTS distance is a few kilometres whereas the distance between a group of BTS’s is much shorter, it does not make sense to draw a point-to-point connection to every BTS. One PCM line has ample capacity to transfer data to several BTSs simultaneously. Therefore, it is possible to draw just one BSC - BTS connection and link the BTSs as a chain. This technique is called "multidrop chain". The BSC sends all the data in one 2Mbit/s PCM line and each BTS in turn analyses the signal, collects the data from the correct timeslots assigned for itself and passes the signal to the next BTS.
But there is one problem with a multidrop chain. Consider what would happen if there is a malfunction somewhere along the line and the chain breaks. More BTSs are isolated and, if the BSC is not informed, it will continue to send data. The solution to this problem is called
"multidrop loop" and instead of a chain we connect the BTSs in the form of a loop.
Previously a dynamic node was needed to split the signal into the two directions around the loop, but later versions of BTS are capable of carrying out this function. The flow of the signal is similar to the signal flow in multidrop chain, except that a BTS will change the “listening” direction if the signal from one side fails. This ensures that the BTSs always receive information from the BSC even if the connection is cut off at some point in the loop.
What is Base Transceiver Station
A base transceiver station is a physical site from where the radio transmission in both the downlink and uplink direction takes place. The radio resources are the frequencies allocated to the Base Station. The particular hardware element inside the Base Transceiver Station (BTS) responsible for transmitting and receiving these radio frequencies is appropriately named "Transceiver (TRX)".
A Base Station site might have any number of TRXs from one to twelve. These TRXs are then configured into one, two or three cells. If a BTS is configured as one cell it is called an "Omnidirectional BTS" and if it is configured as either two or three cells it is called a "Sectorised BTS". In an omnidirectional BTS the maximum number of TRXs is ten, and in a sectorised BTS the maximum number of TRXs is four per sector.
The interface between the BTS and BSC. Generally carried by a DS-1, ES-1, or E1 TDM circuit. Uses TDM subchannels for traffic (TCH), LAPD protocol for BTS supervision and telecom signaling, and carries synchronization from the BSC to the BTS and MS. The interface between the BSC and MSC.
BSC The Base Station Controller (BSC) is in control of and supervises a number of Base Transceiver Stations (BTS). The BSC is responsible for the allocation of radio resources to a mobile call and for the handovers that are made between base stations under his control. Other handovers are under control of the MSC.






9 Comments
Hello writer i am Yolanda Mathew from Vergin Iceland USA , i feel better when i search the topic Transmission Methods Between BSC and BTS in google and i land on your blog , your blog, your information is good ,
ReplyDeleteThank you so much dear Mathew.
DeleteGood info offered here. Good job.
ReplyDeleteThank you for these explanation. But there is something which is still not clear for me.
ReplyDeleteI wish to know if the disruption of communication between BSC and BTS or between NodeB and RNC has an impact on cell availability?
If NodeB's cannot communicate with the RNC, the particular cell will be seen as down and as such can't be said to be available. So, I think such disruption has impacts on the cell availability
DeleteRegardless of whether you are a foodie looking for a culinary involvement with Bangkok's unending cluster of global cafés and customary food shops,am i ugly test
ReplyDeleteRegardless of whether you are a foodie looking for a culinary involvement with Bangkok's unending cluster of global cafés and customary food shops,am i pretty or ugly
ReplyDeleteDeciding to remain at a Hotel Close to Skytrain/BTS is quite possibly the main components to promise you have an agreeable encounter. The BTS, as it's known by local people, is a raised electric train that stumbles into the main business regions in Bangkok, which disney princess are you
ReplyDeletegreat info
ReplyDelete