Posted By: technopediasite
 |
| Metro Ethernet |
Ethernet
History
The
University of Hawaii’s ALOHA network is considered to be the ancestor of all shared
media networks. In 1968, Norman Abramson pioneered the precepts of Ethernet by
developing this packet radio networking system that ran at 4800bp/s and
9600bp/s. A few
years later (1973), Robert Metcalfe and David Boggs at Xerox Corporation in
Palo Alto,
CA applied the ALHOA network principles and created the world’s first Local
Area Network
(LAN). Initially named ALTO ALOHA, the name was later changed to Ethernet.
This first version of Ethernet ran at speeds up to 2.94Mbps. One of the first customers
of Ethernet was the White House – it was used for word processing. Beyond that,
this version of Ethernet was not successfully commercialized.
First
commercial released was by DEC, Intel and Xerox (DIX, the Gang of Three) in 1980
as Ethernet, Version 1 (commonly referred to as Ethernet DIX80). The second revision
release was in 1982 as Ethernet, Version 2 (commonly referred to as Ethernet DIX82).
This is the standard we know today as Ethernet & now Ethernet subdivision
is metro Ethernet. Our main purpose is discuss about the METRO ETHERNET. Now I will try to discuss that "what is Metro Ethernet & what is the benefits of Metro Ethernet in telecom network. Why Metro Ethernet is important in telecom network these days.
What is Metro Ethernet
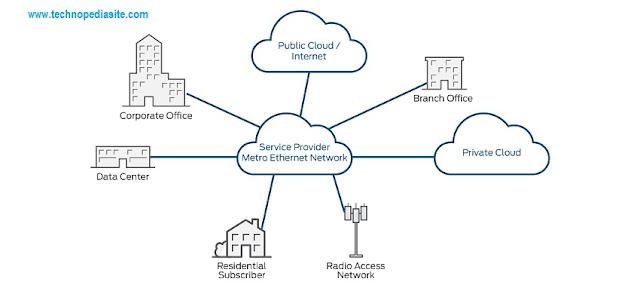 |
| Use of Metro Ethernet |
Metro
Ethernet is the use of Carrier Ethernet technology in metropolitan area
networks (MANs). Because it is typically a collective endeavor with numerous
financial contributors, Metro Ethernet offers cost-effectiveness, reliability,
scalability and bandwidth management superior to most proprietary networks. We can
say in other words that “ Metro Ethernet is an Ethernet transport network that provides point-to-point or multipoint
connectivity services over a metropolitan area network (MAN). Ethernet originated
as a LAN technology, and became a replacement for low-speed WAN technologies.
Metro
Ethernet can connect business local area networks (LANs) and individual end
users to a wide area network (WAN) or to the Internet. Corporations, academic
institutions and government agencies in large cities can use Metro Ethernet to
connect branch campuses or offices to an intranet. use Metro Ethernet to:
➤Interconnect
business offices or data centers. Metro Ethernet can connect two sites or
hundreds of sites.
➤Connect
residential subscribers or businesses to the Internet.
➤Provide
connectivity to public or private cloud data centers.
➤Provide
wholesale mobile backhaul services.
➤Provide
multicast delivery used by business customers for video conferencing, and used
by residential subscribers for IPTV and video applications.
Benefits
of Metro Ethernet
Metro
Ethernet provides the following benefits:
⏩Manage
Risk Smartly :
⏩Flexibility—Supports
a wide variety of services and transports.
⏩Reliability—Ethernet
operations, administration, and maintenance (OAM) performs path discovery,
detects and reports connection failures, and measures performance.
⏩Cost
effectiveness/Ease of Use—Networks are less complicated and easier to maintain
than WAN networks, which lowers equipment and ownership costs.
⏩Quality
of Service (QoS)—Supports QoS features, such as: classification, marking,
policing, queuing, and scheduling.
⏩Scalability—Supports
speeds from one Mbps to 10 Gbps. Customers can increase bandwidth dynamically,
and often without the need to purchase or install new equipment.
Juniper
Networks Metro Ethernet Solutions
Juniper
Networks Metro Ethernet solutions support zero touch deployment and are MEF
CE2.0 certified. This certification:
➤Saves
time and reduces testing costs
➤Provides
faster rollout of services
➤Facilitates
inter-carrier connectivity
Metro
Ethernet Features and Benefits
 |
| Benefits of Metro Ethernet |
Metro
Ethernet over Seamless MPLS : You can run Ethernet services over your MPLS network from the
core to the access segment. It provides service flexibility and scaling of the
MAN where you can terminate Metro Ethernet services at any point in the
network.
Metro
Ethernet over Optical Transport Networks: Juniper Networks product line of BTI
packet optical equipment delivers high-performance for Metro Ethernet services.
ACX
Series Universal Access Routers: These compact, power-efficient, and MEF CE
2.0–certified Carrier Ethernet access and aggregation routers offer rich Layer
2, Layer 3, and MPLS features, programmability, and Ethernet OAM support.
MX Series
Universal 3D Routers: These routers offer high performance for converged residential, mobile,
and Metro Ethernet services on a single platform.
Cloud
Exchange Networks
With
cloud exchange networks (shown in Figure 3), you can augment Ethernet resources
by sharing them with multiple customers. Instead of committing bandwidth to
each customer, you can dynamically allocate bandwidth as needed enabling you to
maximize network utilization and reduce infrastructure costs.
"Pure"
Ethernet technology in the MAN environment is relatively inexpensive compared
with Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SDH) or Multiprotocol Label Switching
(MPLS) systems of similar bandwidth. However, the latter technologies can be
applied to Metro Ethernet in urban areas willing to devote the necessary
financial resources to the task.
Overall
Metro Ethernet was first used outside of the LAN in metropolitan areas, called
MANs (Metropolitan Area Network). We use fiber cabling because of the support
for longer distances.
Metro
Ethernet Services and Topologies
There
are several different Metro Ethernet services, each service has a different
topology. The MEF (Metro Ethernet Forum) is a non-profit consortium that
defines standards and services for Metro Ethernet. In the remaining of this
lesson, we’ll discuss some of the most common services:
➤E-Line
(Ethernet Line Service)
➤E-LAN
(Ethernet LAN Service)
➤E-Tree
(Ethernet Tree Service)
Conclusion
You
have now learned the basics of Metro Ethernet:
⏩Ethernet
technology is interesting because it is used in so many products, making it
cheaper compared to some other technologies.
⏩Ethernet
was first used outside of the LAN in MANs (Metropolitan Area Network), which is why we call it Metro Ethernet.
⏩Ethernet
is also used on WAN connections, which is why we also call it carrier Ethernet.
⏩The provider might use another technology on their network but the end-to-end
protocol in use is Ethernet.




1 Comments
I just want to let you know that I just check out your site and I find it very interesting and informative.. VoIP service providers in India
ReplyDelete