Posted By: technopediasite
Introduction
⏩An IP routing protocol is used within the routing domain (e.g.OSPF,ISIS)
⏩A label distribution protocol is used to distribute address/label mappings between adjacent neighbors
⏩The ingress LSR receives IP packets, performs packet classification (into a FEC), assign a label, and forward the labelled packet into the MPLS network
⏩Core LSRs switch packets/cells based on the label value (no packet classification in the core)
⏩The egress LSR removes the label before forwarding the IP packet outside the MPLS network
Forwarding Equivalence Class
⏩A group of IP packets which are forwarded in the same manner
Over the same path With the same forwarding treatment⏩Packet forwarding consists on
Assign a packet to a FEC
Determine the next-hop of each FEC
⏩MPLS make use of FECs
⏩MPLS nodes assign a label to each FEC
⏩Packet classification (into a FEC) is done where the packet enters the core
⏩No sub-sequent packet classification in the MPLS network
⏩LSP is the unidirectional sequence of LSRs through which the labelled packets have to go through in order to reach the egress LSR
⏩FEC is determined in LSR-ingress
⏩LSPs derive from IGP routing information
⏩LSPs may diverge from IGP shortest path
LSP tunnels (explicit routing) with Traffic Engineering
⏩Generic: can be used over Ethernet, 802.3, PPP links, Frame Relay, ATM PVCs, etc. ⏩Uses new Ethertypes/PPP PIDs/SNAP values/etc.
⏩Label distribution may be upstream or downstream driven
⏩Most implementations use downstream with two variants
Unsolicited Downstream
Downstream on demand
⏩The label at the top of the stack is removed (popped) by the upstream neighbor of the egress LSR
⏩The egress LSR requests the “popping” through the label distribution protocol
⏩Egress LSR advertises implicit-null label
⏩The egress LSR will not have to do a lookup and remove the label itself
⏩One lookup is saved in the egress LSR
⏩Discovery messages
Used to discover and maintain the presence of new peers
Hello packets (UDP) sent to all-routers-in-subnet multicast address
Once neighbor is discovered, the LDP session is established over TCP
⏩Session messages
Establish, maintain and terminate LDP sessions
⏩Advertisement messages
Create, modify, delete label mappings
⏩Notification messages
Error signalling
Introduction
Multiprotocol
Label Switching (MPLS) is a protocol-agnostic routing technique designed to
speed up and shape traffic flows across enterprise and business wide area and
service provider networks.
Application Of MPLS
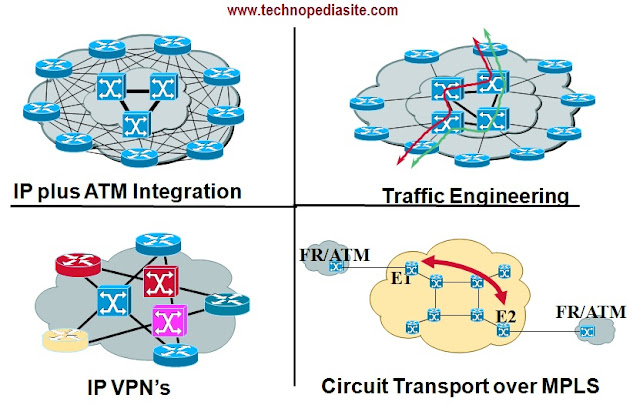 |
| MPLS Network Applications |
MPLS concepts: Label Switch Routers
 |
| MPLS Concept Label Switch Routers |
⏩A label distribution protocol is used to distribute address/label mappings between adjacent neighbors
⏩The ingress LSR receives IP packets, performs packet classification (into a FEC), assign a label, and forward the labelled packet into the MPLS network
⏩Core LSRs switch packets/cells based on the label value (no packet classification in the core)
⏩The egress LSR removes the label before forwarding the IP packet outside the MPLS network
Packet
forwarding: FEC and Next-Hop
⏩IP packets are classified in FECs Forwarding Equivalence Class
⏩A group of IP packets which are forwarded in the same manner
Over the same path With the same forwarding treatment⏩Packet forwarding consists on
Assign a packet to a FEC
Determine the next-hop of each FEC
⏩MPLS make use of FECs
⏩MPLS nodes assign a label to each FEC
⏩Packet classification (into a FEC) is done where the packet enters the core
⏩No sub-sequent packet classification in the MPLS network
 |
| Packet forwarding: FEC and Next-Hop |
Label
Switch Path (LSP)
⏩LSP is the unidirectional sequence of LSRs through which the labelled packets have to go through in order to reach the egress LSR
⏩FEC is determined in LSR-ingress
 |
| MPLS Label Switch Path (LSP) |
⏩LSPs may diverge from IGP shortest path
LSP tunnels (explicit routing) with Traffic Engineering
MPLS
concepts Labels
⏩Can have label stacking of 4 octets each
⏩draft-ietf-mpls-label-encaps-07.txt
⏩Labels have local significance
Each LSR binds his own label mappings
⏩Each LSR assign labels to his FECs
⏩Labels are assigned and exchanged between adjacent LSRs
Downstream to Upstream
⏩Applications may require non-adjacent neighbors e.g VPN
⏩Several protocols for label exchange
⏩LDP - Maps unicast IP destinations into labels
⏩RSVP, CR-LDP - Used for traffic engineering and resource reservation
⏩BGP - External labels (VPN)
⏩Rtr-C is the downstream neighbor of Rtr-B for destination 171.68.10/24
⏩Rtr-B is the downstream neighbor of Rtr-A for destination 171.68.10/24
⏩LSRs know their downstream neighbors through the IP routing protocol
⏩Next-hop address is the downstream neighbor
⏩LSRs assign a label to each FEC⏩Labels have local significance
Each LSR binds his own label mappings
⏩Each LSR assign labels to his FECs
⏩Labels are assigned and exchanged between adjacent LSRs
Downstream to Upstream
⏩Applications may require non-adjacent neighbors e.g VPN
Label
Distribution Protocols
⏩Several protocols for label exchange
⏩LDP - Maps unicast IP destinations into labels
⏩RSVP, CR-LDP - Used for traffic engineering and resource reservation
⏩BGP - External labels (VPN)
Upstream
and Downstream LSRs
⏩Rtr-B is the downstream neighbor of Rtr-A for destination 171.68.10/24
⏩LSRs know their downstream neighbors through the IP routing protocol
⏩Next-hop address is the downstream neighbor
⏩Label distribution may be upstream or downstream driven
⏩Most implementations use downstream with two variants
Unsolicited Downstream
Downstream on demand
Penultimate
Hop Popping
⏩The egress LSR requests the “popping” through the label distribution protocol
⏩Egress LSR advertises implicit-null label
⏩The egress LSR will not have to do a lookup and remove the label itself
⏩One lookup is saved in the egress LSR
⏩Egress
LSR needs to do an IP lookup for finding more specific route
⏩Egress
LSR need NOT receive a labelled packet-label
will have to be popped anyway
 |
| MPLS Penultimate Hop Popping |
LDP Concepts
⏩One of several standardised label
distribution protocol
draft-ietf-mpls-ldp-09.txt
⏩A set of procedures and messages to
distribute mappings between labels and FECs
⏩Two LSRs which use LDP to exchange
label/FEC mapping information are known as "LDP Peers"
⏩Peers exchange LDP messages
⏩Uses TLV encoded message structure
Used to discover and maintain the presence of new peers
Hello packets (UDP) sent to all-routers-in-subnet multicast address
Once neighbor is discovered, the LDP session is established over TCP
⏩Session messages
Establish, maintain and terminate LDP sessions
⏩Advertisement messages
Create, modify, delete label mappings
⏩Notification messages
Error signalling






1 Comments
very helpful
ReplyDelete