Posted By: Technopediasite.com

An optical fiber is made of very thin glass rods composed of two parts: the inner portion of the rod or core and the surrounding layer or cladding. Light injected into the core of a glass fiber will follow the physical path of that fiber due to the total internal reflection of the light between the core and the cladding. A plastic sheathing around the fiber provides the mechanical protection.
Principle of the transmission:
* a ray of light enters into the fiber at a small angle a.
* the capability (maximum acceptable value) of the fiber cable to receive light on its core is determined by its numerical aperture NA:
NA= (n12 –n22)1/2
•Numerical aperture (NA): NA= (n12 –n22)1/2
•Typical NA values are 0.1 to 0.4 which correspond to acceptance angles of 11 degrees to 46 degrees
•Acceptance angle of a fiber: qa = sin-1 NA
•Light that enters at an angle equal to or less than the acceptance angle will be guided
•NA is more means more light gathering power

Velocity:
The velocity at which light travels through a medium is determined by the refractive index of the medium. The refractive index (n) is a unitless number which represents the ratio of the velocity of light in a vacuum to the velocity of the light in the medium.
n=c/v
where:n: Refractive Index
c: Speed of light in a vacuum (approximately 3 x 10 squre 8 m/s)
V: Speed of light in the transmission medium.
Typical values of n lie between 1.45 and 1.55.
Light entering with different angles does not follow the same path. Light entering the center of the fiber core at a very low angle will take a relatively direct path through the center of the fiber. Light injected at a high angle of incidence or near the outer edge of the fiber core will take a less direct, longer path through the fiber and therefore travel more slowly down the
length of the fiber. Each path resulting from a given angle of incidence and entry point can give rise to a mode. As they travel along the fiber, all the modes are attenuated.
Attenuation:
The attenuation in a fiber is caused by different factors:
Light Absorption: Absorption may be defined as the conversion of light energy to heat, and is related to the resonances in the fiber material. There are intrinsic absorptions (due to fiber material and molecular resonance) and extrinsic absorptions (due to impurities such as OH- ions at around 1240 nm and 1390 nm). In modern fibers, extrinsic factors are almost negligible.
Rayleigh scattering: Scattering, primarily Rayleigh scattering, also contributes to attenuation. Scattering causes the light energy to be dispersed in all directions, with some of the light escaping the fiber core. A small portion of this light energy is returned down the core and is termed - back scattering.
Bending Losses: which are caused by light escaping the core due to imperfections at the core/clad boundary (microbending), or the angle of incidence of the light energy at the core/cladding boundary exceeding the Numerical Aperture (internal angle of acceptance) of the fiber due to bending of the fiber (macrobending). Singlemode fibers (for example) may be bent to a radius of 10 cm with no significant losses, however after the minimum bend radius is exceeded, losses increase exponentially with increasing radius. Minimum bend radius is dependent on fiber design and light wavelength.
For a fiber optic span, passive components and connection losses have to be added to obtain the total signal attenuation.
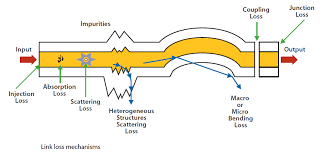
The attenuation, for a given wavelength, is defined as the ratio between the input power and the output power of the fiber being measured. It is generally expressed in decibels (dB).
This attenuation depends on the fiber and on the wavelength. For example, Rayleigh scattering is inversely proportional to the fourth power of the wavelength. If we look at the absorption spectrum of a fiber against the wavelength of the laser, we can notice some characteristics.
Why Cladding is required?
* Mechanical protection.
* Guard against electromagnetic interference
It is necessary to keep the light reflecting in core instead of being refracted, because we need it to pass on to destination from source. And when light enters from denser material into less dense material the cladding so it changes its angel, it reflects back the light in core. This is the reason that core is denser and outer layer is less dense.
An optical fiber is made of very thin glass rods composed of two parts: the inner portion of the rod or core and the surrounding layer or cladding. Light injected into the core of a glass fiber will follow the physical path of that fiber due to the total internal reflection of the light between the core and the cladding. A plastic sheathing around the fiber provides the mechanical protection.
Principle of the transmission:
* a ray of light enters into the fiber at a small angle a.
* the capability (maximum acceptable value) of the fiber cable to receive light on its core is determined by its numerical aperture NA:
NA= (n12 –n22)1/2
•Numerical aperture (NA): NA= (n12 –n22)1/2
•Typical NA values are 0.1 to 0.4 which correspond to acceptance angles of 11 degrees to 46 degrees
•Acceptance angle of a fiber: qa = sin-1 NA
•Light that enters at an angle equal to or less than the acceptance angle will be guided
•NA is more means more light gathering power

Light propagation:
If a > a0: the ray is fully refracted and not captured by the core.
Refraction :
n1 sin Φ1 = n2 sinΦc
If a < a0: the ray is reflected and remains in the core
Reflection :
Φ1 = Φc
Velocity:
The velocity at which light travels through a medium is determined by the refractive index of the medium. The refractive index (n) is a unitless number which represents the ratio of the velocity of light in a vacuum to the velocity of the light in the medium.
n=c/v
where:n: Refractive Index
c: Speed of light in a vacuum (approximately 3 x 10 squre 8 m/s)
V: Speed of light in the transmission medium.
Typical values of n lie between 1.45 and 1.55.
Light entering with different angles does not follow the same path. Light entering the center of the fiber core at a very low angle will take a relatively direct path through the center of the fiber. Light injected at a high angle of incidence or near the outer edge of the fiber core will take a less direct, longer path through the fiber and therefore travel more slowly down the
length of the fiber. Each path resulting from a given angle of incidence and entry point can give rise to a mode. As they travel along the fiber, all the modes are attenuated.
Attenuation:
The attenuation in a fiber is caused by different factors:
Light Absorption: Absorption may be defined as the conversion of light energy to heat, and is related to the resonances in the fiber material. There are intrinsic absorptions (due to fiber material and molecular resonance) and extrinsic absorptions (due to impurities such as OH- ions at around 1240 nm and 1390 nm). In modern fibers, extrinsic factors are almost negligible.
Rayleigh scattering: Scattering, primarily Rayleigh scattering, also contributes to attenuation. Scattering causes the light energy to be dispersed in all directions, with some of the light escaping the fiber core. A small portion of this light energy is returned down the core and is termed - back scattering.
Bending Losses: which are caused by light escaping the core due to imperfections at the core/clad boundary (microbending), or the angle of incidence of the light energy at the core/cladding boundary exceeding the Numerical Aperture (internal angle of acceptance) of the fiber due to bending of the fiber (macrobending). Singlemode fibers (for example) may be bent to a radius of 10 cm with no significant losses, however after the minimum bend radius is exceeded, losses increase exponentially with increasing radius. Minimum bend radius is dependent on fiber design and light wavelength.
For a fiber optic span, passive components and connection losses have to be added to obtain the total signal attenuation.
The attenuation, for a given wavelength, is defined as the ratio between the input power and the output power of the fiber being measured. It is generally expressed in decibels (dB).
This attenuation depends on the fiber and on the wavelength. For example, Rayleigh scattering is inversely proportional to the fourth power of the wavelength. If we look at the absorption spectrum of a fiber against the wavelength of the laser, we can notice some characteristics.
Why Cladding is required?
* Mechanical protection.
* Guard against electromagnetic interference
There are two layers of optical fiber, the inner layer and the outer layer. A data travel through inner layer which is consisting of central hollow material is known as core which is denser; it’s made of either glass or a plastic. This core is covered by a less dense material known as cladding the outer layer that can also be made of glass of a plastic. Cladding and core as made of less dense and denser material respectively with such a combination (adjustment of density) that helps the light to reflect back to the inner surface of core. It doesn’t allow the light to refract. And light keep goes on towards destination.
Purpose of cladding in an optical fiber:
It is necessary to keep the light reflecting in core instead of being refracted, because we need it to pass on to destination from source. And when light enters from denser material into less dense material the cladding so it changes its angel, it reflects back the light in core. This is the reason that core is denser and outer layer is less dense.




4 Comments
هل تبحث عن شركات كلادينج هناك اكثر
ReplyDeleteهناك اكثر من شركة كلادينج و تعتبر شركة سيستم بنل من افضل شركات تركيب كلادينج واجهات ليدنا مجموعة رائعة من العروض و الخصومات المميزة تواصل معنا و احصل على خصم رائع
ReplyDeleteعند تعاملك مع مصنع اثاث مكتبي كواحد من أفضل مصنع اثاث مكتبى في مصر فانك ستحصل علي منتجات بجودة عالية ومتانة قياسية في وقت محدد , كما أنك ستجد ضمان وجودة , وهذا ما لا يتوافر في العديد من مصانع الاثاث في مصر ونقدم لك بعض النصائح عن القيام بي اختيار قطع الاثاث المكتبي طاولة المكتب اثناء القيام بي اختيار عليك الحرص علي اختيار طاولة مكتبة مناسبة مع مساحة المكان و باقي الادوات المكتبية .
ReplyDelete
ReplyDeleteإذا كنت تبحث عن شركة أثاث مكتبي لها ثقه كبيره ف شركة وود أند ديزاين، هي المكان الصحيح شركة شركات اثاث مكتبي كلاسيك. نحن متخصصون في توفير أثاث مكتبي عالي الجودة وبأسعار مناسبة. نعتقد أن كل شخص يستحق أن يكون لديه مكتب مريح ولامع، لذلك نقدم مجموعة واسعة من خيارات الأثاث للاختيار من بينها. نقدم أيضًا ضمان الرضا بنسبة 100٪ بحيث يمكنك التأكد من أنك تتخذ القرار الأفضل لمكتبك.